Few-Shot 2D Echo to 3D Cardiac Reconstruction via Neural Implicit Priors
Course Project for Learning for 3D Vision
project status: completed —
Developed a unified framework to reconstruct patient-specific 3D ventricular shapes from sparse 2D echocardiography views. Moving beyond simple per-scan optimization, this work introduces a Test-Time Optimization strategy where a globally learned neural shape prior is fine-tuned on sparse patient data. This approach combines the generalization power of dataset-wide learning with the precision of patient-specific optimization. The core innovation is a “Hybrid” learning strategy that alternates between estimating slice poses and refining a 3D Implicit Neural Representation (INR). The framework supports three distinct operating modes to balance speed and accuracy:
Frameworks
- Local: Trains a fresh INR from scratch for every single patient. Accurate but slow and prone to overfitting sparse views.
- Global: Learns a single shared cardiac shape prior across the entire training population. Fast inference but lacks patient-specific detail.
- Mixed (Proposed):
- Pre-training: A global shape prior is learned on the training set.
- Inference: For a new, unseen patient, we initialize the network with the global prior and run a rapid “refinement” optimization loop on the patient’s sparse 2D slices. This adapts the generic heart shape to fit the specific patient’s anatomy in real-time.
Architecture
- Representation: Coordinate-based Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) representing occupancy signed distance function.
- Differentiable Rendering: A custom vectorized projection layer maps the 3D implicit shape to 2D slice planes (A2C, A4C, PSAX) for direct supervision against clinical contours.
- Pose Refinement: Jointly optimizes rigid slice pose parameters (SE(3)) alongside shape, correcting for acquisition misalignment.
- Meta-Learning Approach (Reptile): Implementation of Reptile-based meta-learning to find an initialization that adapts rapidly to new cardiac geometries with minimal gradient steps.
Observations
- Test-Time Refinement: Demonstrates that “overfitting” to a specific patient at test time (via fine-tuning) significantly boosts reconstruction accuracy compared to static inference.
- Implicit Shape Priors: Uses population-level learning to regularize reconstruction in regions where 2D data is missing, preventing the “shape explosion” common in sparse-view reconstruction.
- Strict Slice Selection: Automated stratifiction strategy to select optimal diagnostic views (ED/ES frames) from raw volumetric data.
- Clinical Validation: Evaluates performance using rigorous medical metrics: 3D Dice Coefficient, IoU (Intersection over Union), and clinical volume estimation (End-Diastolic/End-Systolic volumes).
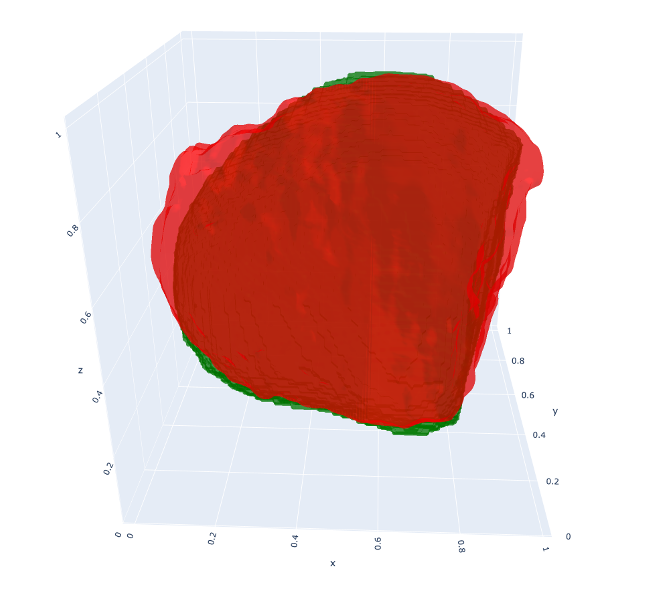
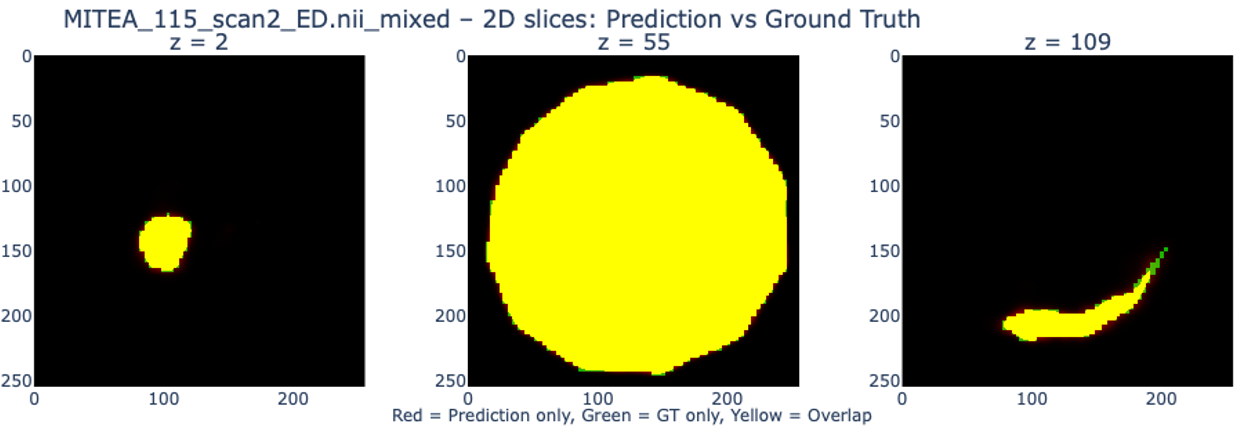
The method bridges the gap between widely available 2D ultrasound and expensive 3D imaging. By leveraging Test-Time Optimization, we achieve high-fidelity 3D meshes from as few as 3 standard views. The framework handles the inherent sparsity of echocardiography by relying on the learned global prior to “hallucinate” plausible geometry in unobserved regions, while the patient-specific refinement ensures the reconstruction adheres tightly to the observed clinical data.
Collaborators: Vivek Dhara and Vaibhav Parekh