project status: completed and published/presented. —
My undergraduate research was anchored and centered around my work with building deep learning models that combined explainable AI with attention mechanisms for robust neural networks that visually explained model predictions. I paired this with my work in image pre-processing for improving training using feature engineering and removing training biases.
!
The work utilized the LC25000 dataset on two studies: one where I created a baseline results for the 5-way classification (Nayak et al., 2023) and the other being a more fleshed out work with the lung cancer dataset and transfer learning coupled with spatial attention (Nayak et al., 2024).
References
2024
-
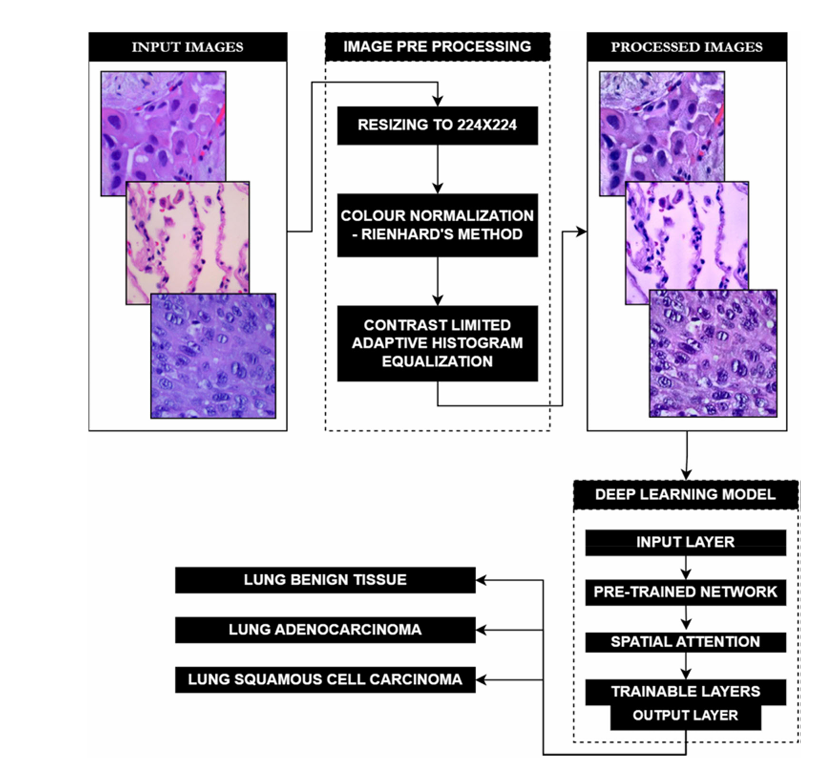
Automated histopathological detection and classification of lung cancer with an image pre-processing pipeline and spatial attention with deep neural networks
Tushar Nayak, Nitila Gokulkrishnan, Krishnaraj Chadaga, and 3 more authors
Cogent Engineering, 2024

Lung Cancer is a major cancer in the world and specifically India. Histopathological examination of tumorous tissue biopsy is the gold standard method used to clinically identify the type, sub-type, and stage of cancer. Two of the most prevalent forms of lung cancer: Adenocarcinoma & Squamous Cell Carcinoma account for nearly 80% of all lung cancer cases, which makes classifying the two subtypes of high importance. Proposed in this study is a data pre-processing pipeline for the H&E-stained lung biopsy images along with a customized EfficientNetB3-based Convolutional Neural Network employing spatial attention, trained on a public three-class lung cancer histopathological image dataset. The pre-processing pipeline employed before training, validation and testing helps enhance features of the histopathological images and removes biases due to stain variations for increased model robustness. The usage of a pre-trained CNN helps the deep learning model generalize better with the pre-trained weights, while the attention mechanism On three-fold validation, the classifier bagged accuracies of 0.9943 ± 0.0012 and 0.9947 ± 0.0018 and combined F1-Scores of 0.9942 ± 0.0042 and 0.9833 ± 0.0216 over the validation and testing data respectively. The high performance of the model combined with its computational efficiency could enable easy deployment of our model without necessitating infrastructure overhaul.
2023
-
Processing and Detection of Lung and Colon Cancer from Histopathological Images using Deep Residual Networks
Tushar Nayak, Niranjana Sampathila, and Nitila Gokulkrishnan
In 2023 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Computing and Communication Technologies (CONECCT), 2023
Lung & Colon cancer are amongst the leading cause of cancer related deaths worldwide. In this study, we used a five-class lung and colon cancer histopathology dataset and applied various image preprocessing techniques such as contrast stretching, unsharp masking, and resizing. We then trained a ResNetl01 model on this preprocessed dataset and achieved a high accuracy of 99.7%. The increased reliability and robustness of deep learning-based histopathology classifiers with high performance computers can enable instantaneous and automated diagnosis which can further help treatment and recovery.